Modern manufacturing is a complex industry, demanding precision, efficiency, collaboration, and adaptability. In this article we examine costly manufacturing problems including human error, workforce challenges, and technology issues. Then, we offer practical solutions and strategies to address these costly manufacturing problems, improve efficiency, and help companies reach their full potential.
Human Error
Human error, or rather high rates of human error, is one of the costliest manufacturing problems. The most obvious result of human error is a defective product. A mistake made on the production floor results in scrap (wasted material and time), rework (wasted time), or if the human error goes undetected, the defective product can lead to customer dissatisfaction. Human errors can create safety issues and increased costs due to wasted materials and lost productivity. They can also cause production delays–23% of unplanned downtime in manufacturing is caused by human error
Causes of Human Error
What causes human errors in manufacturing? Accidents and missteps are going to happen, but there are contributing factors that make them more likely. Reducing human errors and their associated costs requires an understanding of why these errors occur in the first place.
- Inadequate Training
- Unclear Instructions: ambiguous or difficult to see/interpret
- Lack of Knowledge/Skill
- Fatigue and Stress
- Poor Work Environment: distracting, cramped, or poorly designed workspaces
- Poorly Designed Processes
Ways to Reduce Human Errors in Manufacturing
Mistakes are an inevitable part of being human, so addressing human errors in manufacturing is about reduction not perfection. These strategies can help reduce human errors in manufacturing.
- Enhance training and education procedures. Training also reduces employee turnover, so you’ll have more experienced employees on the floor.
- Provide clear instructions. Detailed digital work instructions and visual aids are especially helpful.
- Identify and address problem areas.
- Establish clear standard operating procedures (SOPs) for all tasks.
- Utilize technology to improve processes and communication down the line.
- Encourage open communication so problems and concerns can be addressed early.
Workforce Challenges
A quality workforce is essential to the success of a company regardless of industry. Workforce challenges are a critical concern across the manufacturing industry, impacting productivity, growth potential, and innovation. Let’s look at the top workforce challenges in manufacturing.
An Aging Workforce
- Mass Retirement: A significant percentage of the manufacturing workforce is approaching retirement, which means a loss of expertise and a scramble to replace them.
- Technology Skills Gap: The rapid advancement and integration of new technologies such as automation, AI, and robotics requires new skills that many manufacturing workers lack. Manufacturers must find new workers who have the skillset to keep up with new tech and train existing workers who do not.
- Resistance to Tech: Seasoned employees, specifically older workers, often create a workplace culture that opposes new technology because they are uncomfortable or unwilling to accept changes.
Solutions for An Aging Workforce
The aging workforce in manufacturing is a tough reality, but it can be handled with grace. The only solution for mass retirement is hiring new people, but we will discuss that more in the next section. As far as the technology skills gap and the resistance to tech, there are two strategies to make the transition smoother for your company and older workers.
- Explain the value of new tech. Employees are more likely to resist technological advancements if they don’t understand why they’re being implemented. Explain the reasons behind the new technology. For example, how will it make their lives easier, improve the company, and/or address problems?
- Provide adequate training. Much of the resistance to tech among older generations is because they are simply uncomfortable due to their lack of knowledge/experience. Providing excellent training gives hesitant employees the confidence and skills they need to succeed with new tech.
Recruitment Challenges
- Lack of Interest among Young Adults: Members of younger generations tend to view the manufacturing industry as undesirable or outdated, making it difficult to recruit young job applicants.
- Competitive Job Market: Skilled workers are in high demand, so the manufacturing job market is highly competitive. Attracting and retaining skilled workers is a challenge many manufacturers face.
Strategies to Overcome Recruitment Challenges
Now that we understand the main recruitment challenges in manufacturing, let’s discuss strategies for overcoming them.
- Show that manufacturing is a high-tech field: Of course, this strategy only works if your company is technologically advanced. Showcasing the impressive science and cutting-edge technology involved in manufacturing via your website, in job postings, or during hiring opportunities such as job fairs will help you hire! Things like digital work instructions, data-driven production, state-of-the-art tools and machinery can repaint the way young people view manufacturing and improve your odds of attracting skilled candidates in a competitive market.
- Offer competitive wages and benefits: To acquire skilled and younger workers, you might have to step up your game in terms of wages and benefits. Millennials and Gen Z expect more from employers compared to previous generations, and failing to meet their standards can cause your workforce to dwindle. Skilled workers have a lot of employment options, so fair wages and good benefits are necessary for them to even consider your company.
Technology and Data Issues
Today, manufacturing relies heavily on technology and data. While in this digital age, technological advancements and the ability to record and utilize data like never before are generally positive, they also introduce new challenges. The following technology and data issues can be costly if not addressed.
Cybersecurity Breaches
Most manufacturers rely on the internet and software programs to direct operations. However, relying on the internet, specifically if your company utilizes cloud computing and cloud storage, opens you up to external threats. Cyber security attacks are nerve racking and costly. Ransomware attacks can encrypt your critical systems and lead to production halts and costly downtime. If a hacker breaks into your computer system, they can steal intellectual property such as product designs, sensitive data, or even shut down your system and demand a ransom payment to restore it. Cybersecurity breaches can put your customers and staff at risk. Industrial Control Systems (ICS) attacks can manipulate machinery which interrupts production, but more importantly, can put your workers in harm’s way.
Preventing Cybersecurity Breaches
There is no surefire way to fend off 100% of cybersecurity breaches, but there are steps you can take to fortify your business.
- Strong Cybersecurity Infrastructure: Firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) act as a barrier between your internal network and external threats, blocking and monitoring suspicious traffic.
- Utilize Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to provide secure remote access for employees.
- Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities.
- Data Protection: Encrypt sensitive data and limit access to authorized personnel. Regularly back up critical data and have a recovery plan in place in case of a breach.
- Employee Training: Provide basic cybersecurity training to educate employees about cybersecurity threats such as phishing. Develop and enforce clear cybersecurity policies and procedures for employees to follow.
Data Inaccuracies or Failure to Record Data
Revolutionary manufacturing technologies, like software linking engineers to the production floor, advanced data analysis programs, and instantly updatable digital work instructions, are powerful tools. However, their effectiveness hinges on the quality of the underlying data. Accurate data is the essential ingredient for driving true manufacturing efficiency. Data inaccuracies and failure to record data can lead to inappropriate and costly changes on the manufacturing floor. Incorrect data means less efficient operations—wasted time and money.
Strategies to Improve Data Collection
- Stressing the Importance of Data: The importance of accurate data should be stressed to every person from the manufacturing floor to the C-suite to create an efficient operation.
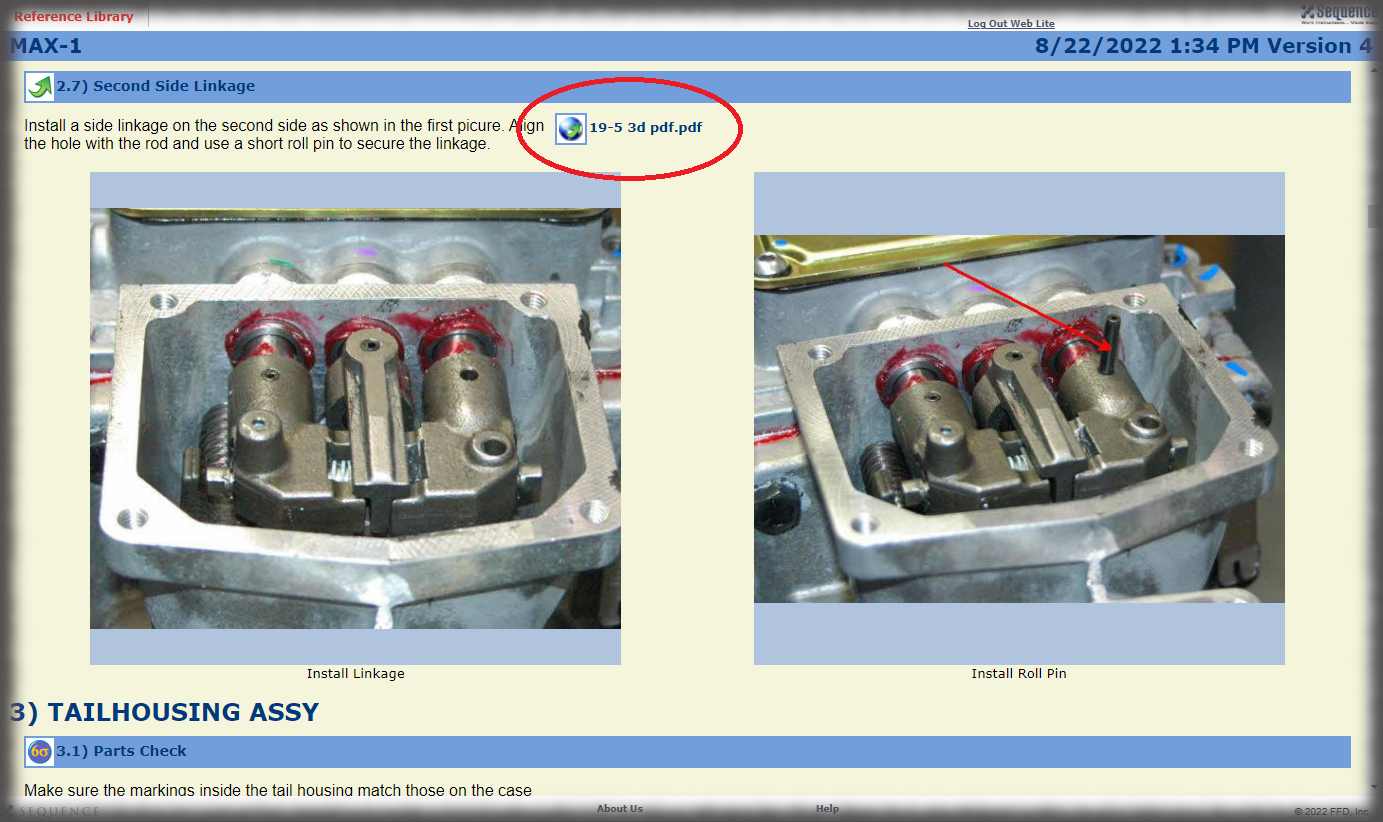
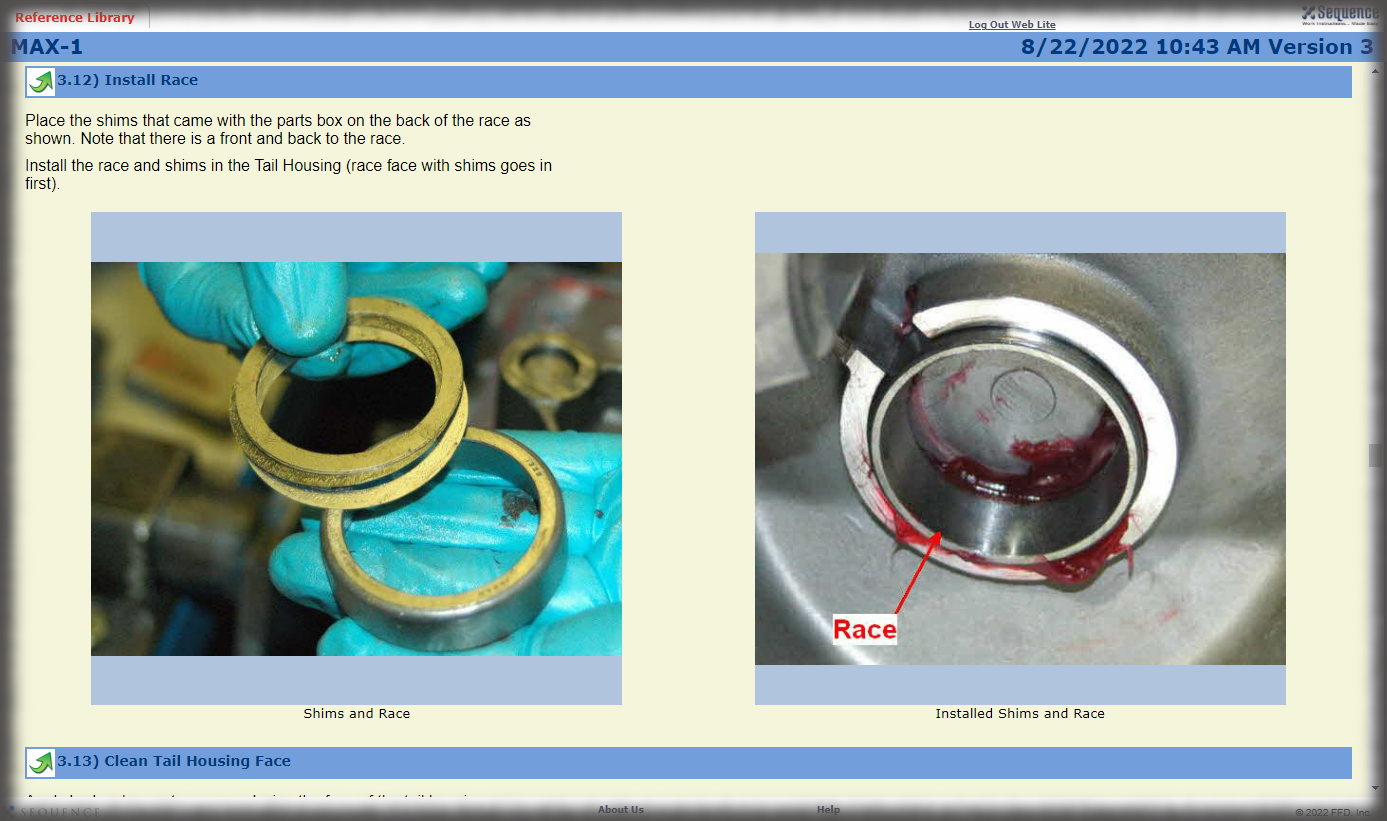
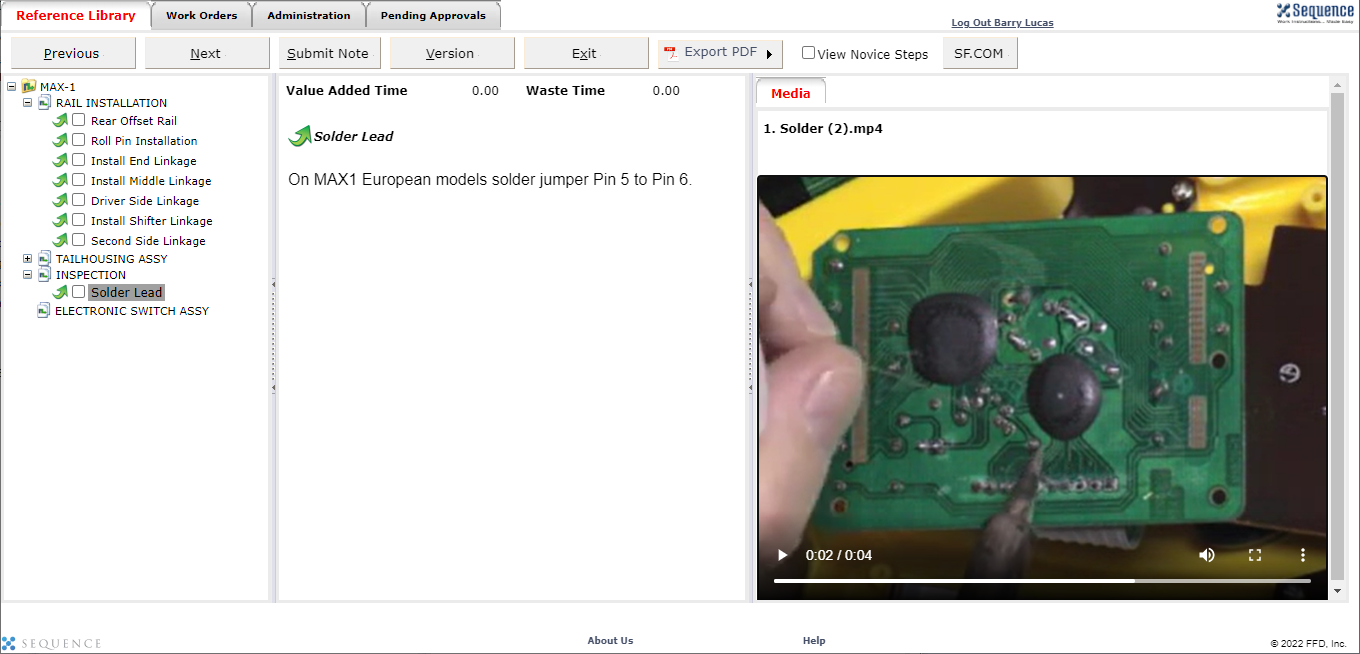
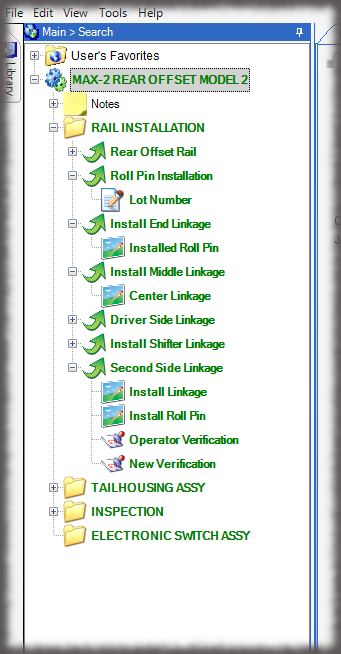
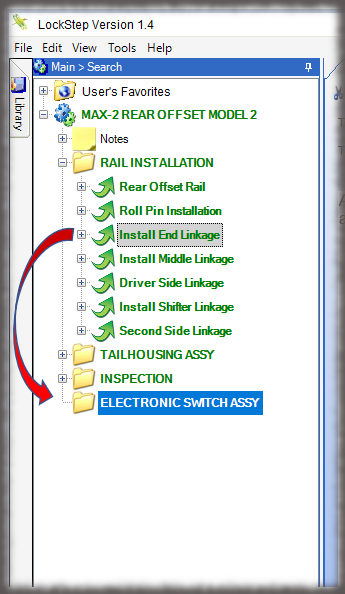
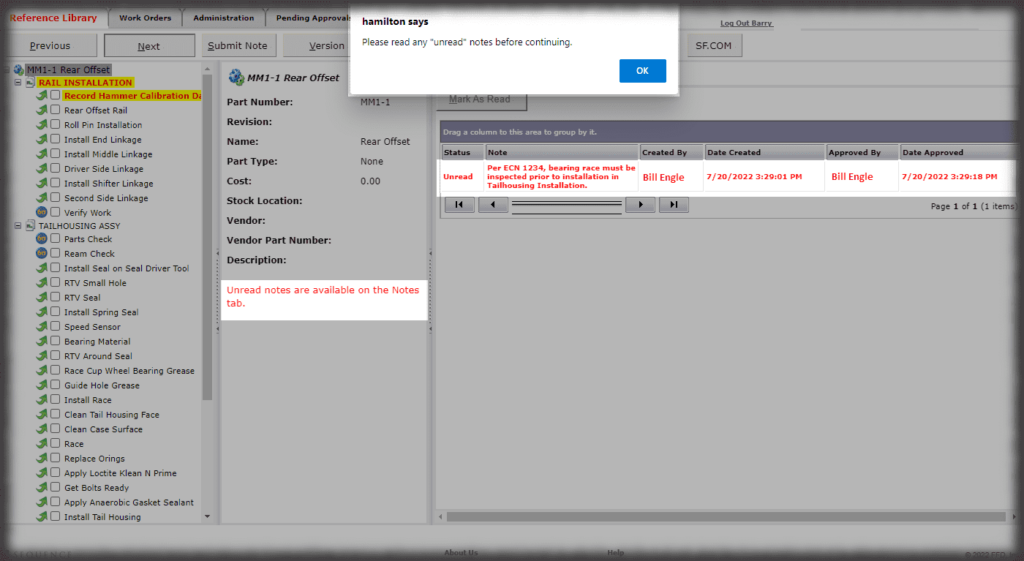
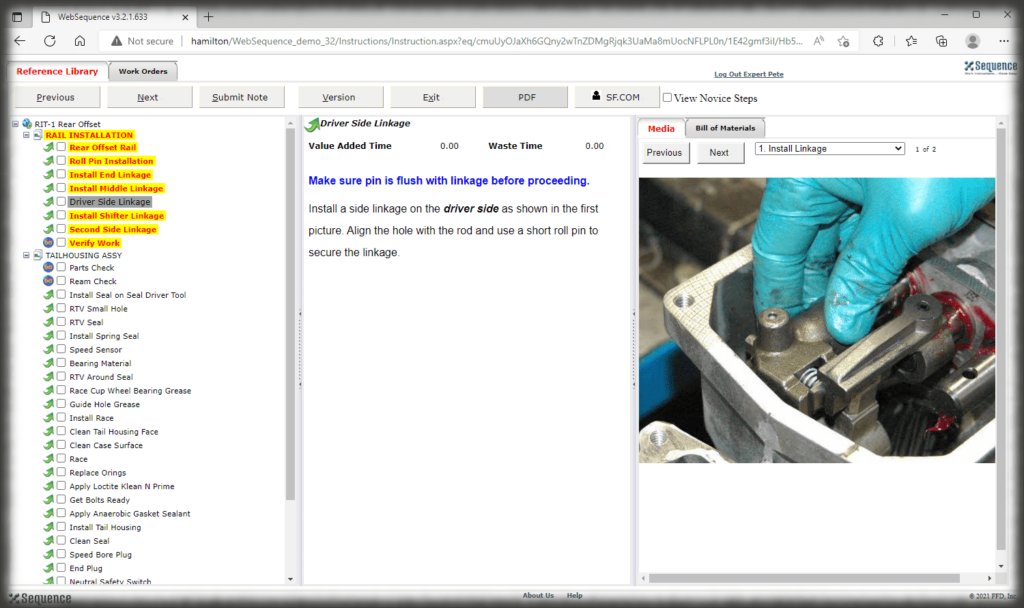
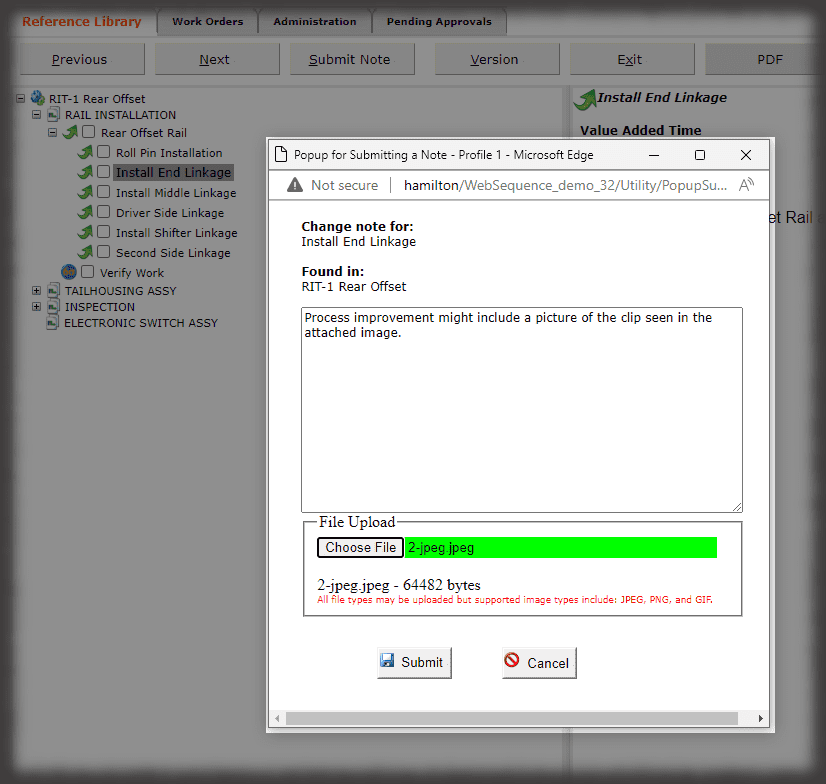
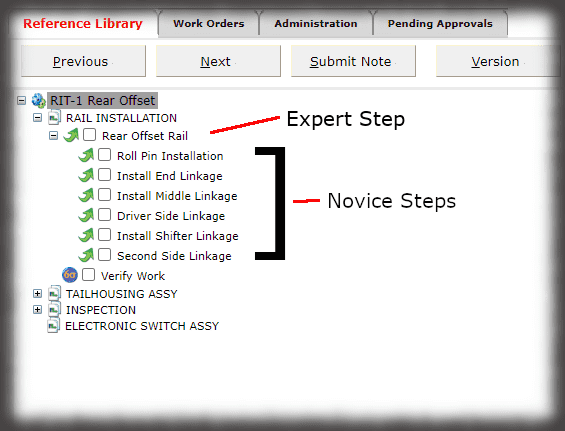
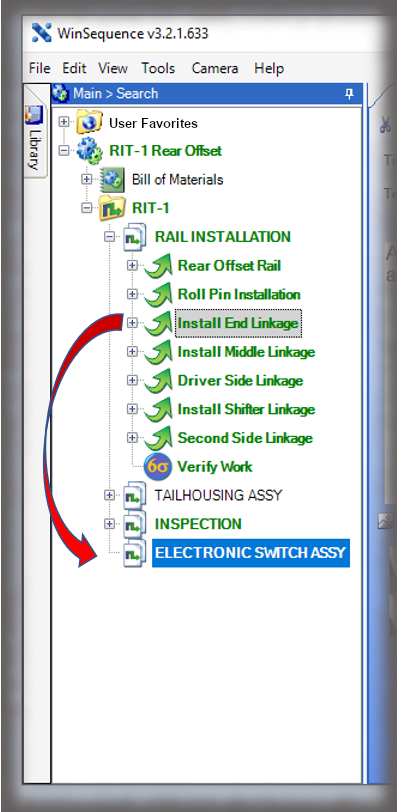
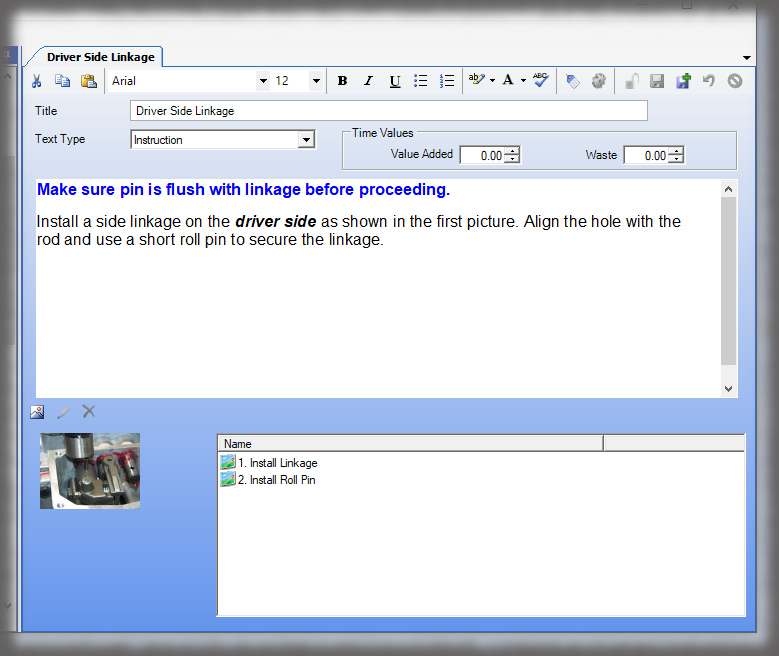
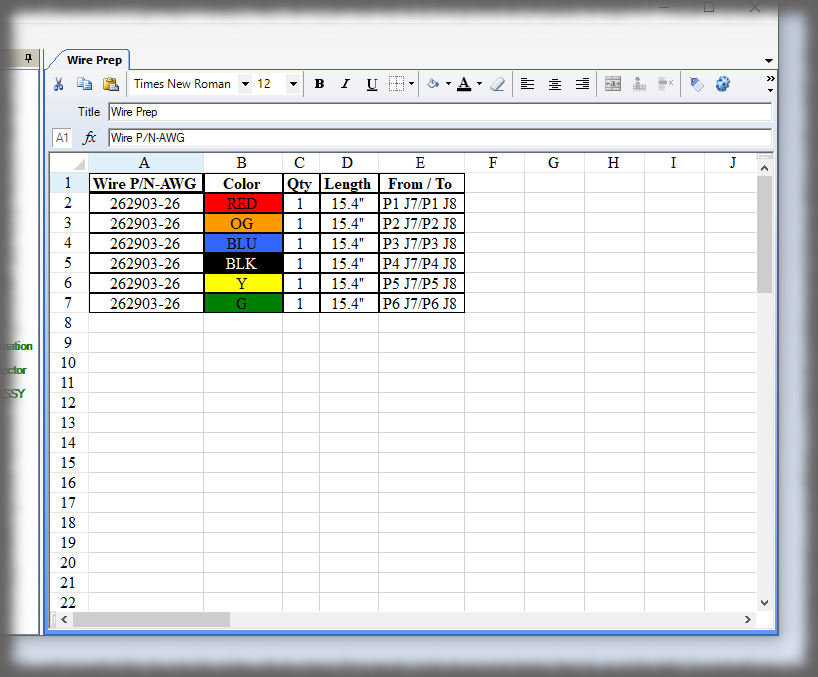
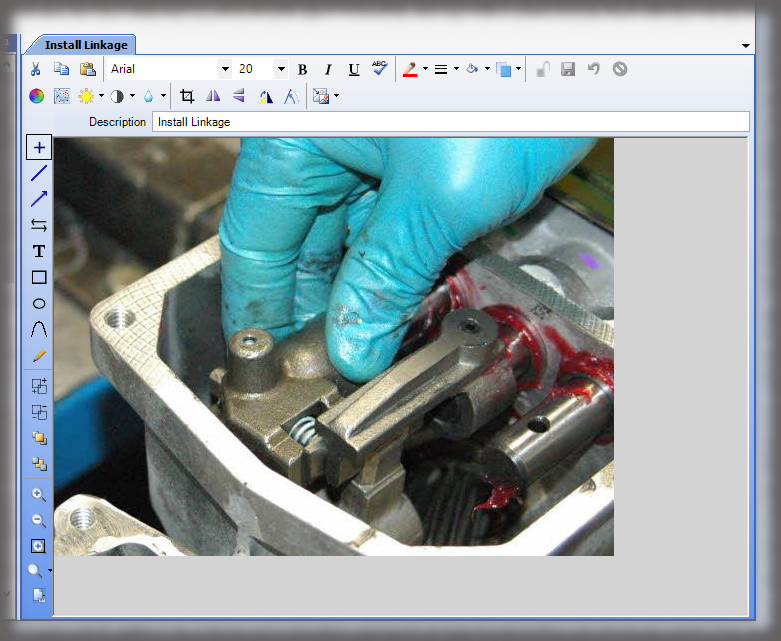
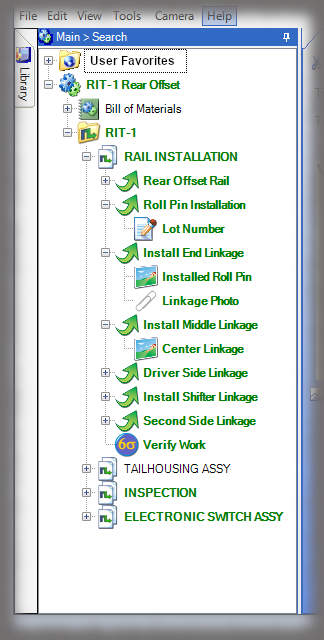
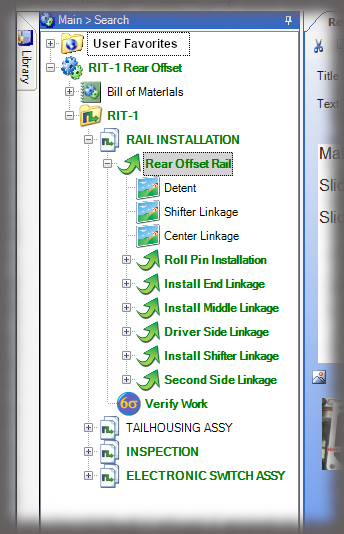
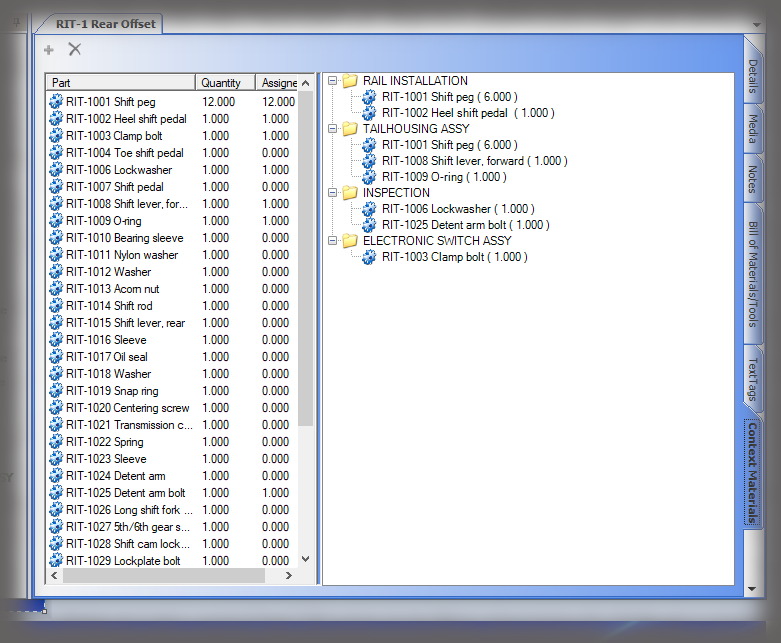
- Digital Work Instructions: Digital work instructions are a great way to ensure that data is always recorded and recorded correctly. With digital work instructions, data can be recorded instantly as workers click to move from one step to another. If a manual measurement is required, such as temperature, DWIs can require workers to enter that figure before moving onto the next step. If something unusual occurs on the production line or a worker recognizes an opportunity for improvement, they have the power to record and submit that information at their fingertips.
Stuck in the Past: Failure to Adopt New Manufacturing Technologies
The failure to evolve puts manufacturers at a competitive disadvantage. Precision, efficiency, continuous analysis and improvement are keys to success in modern manufacturing. Technology can improve your business’s performance in each of these categories. The failure to adopt new manufacturing technologies will make long-term success very difficult.
Explore the Benefits of New Manufacturing Technologies
Conduct research on new technologies available in your industry to understand the potential benefits. Reach out to experts to learn how these technologies can help your business specifically. If you think new tech isn’t worth it, consulting the experts to see the numbers and possibilities might surprise you and change your perspective!
Experience the Benefits of Visual Work Instructions
Visual Work Instructions, also known as Digital Work Instructions (DWIs), can help you address many of the costly problems discussed in this blog. Digital Work Instructions provide clear, step-by-step visual instructions, and videos. The level of detail reduces human errors and their associated costs and makes training new employees quick and simple. They are easy to use, even for workers who are not technologically inclined. Digital Work Instructions connect all relevant parties so they can collaborate and communicate virtually. Data can be collected in real-time and changes to the DWIs can be made instantly to maximize efficiency. The benefits of Visual Work Instructions don’t stop there.
Sequence Software offers an impressive line of visual work instruction products that are user-friendly, scalable, and compatible with a wide range of industries. Find out more about Visual Work Instructions and request a demo today.